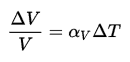Changes of Density
In general, density can be changed by changing either the pressure or the temperature. Increasing the pressure always increases the density of a material. The effect of pressure on the densities of liquids and solids is very very small. On the other hand, the density of gases is strongly affected by pressure. This is expressed by compressibility. Compressibility is a measure of the relative volume change of a fluid or solid as a response to a pressure change.
The effect of temperature on the densities of liquids and solids is also very important. Most substances expand when heated and contract when cooled. However, the amount of expansion or contraction varies, depending on the material. This phenomenon is known as thermal expansion. The change in volume of a material which undergoes a temperature change is given by following relation:
where ∆T is the change in temperature, V is the original volume, ∆V is the change in volume, and αV is the coefficient of volume expansion.
It must be noted, there are exceptions from this rule. For example, water differs from most liquids in that it becomes less dense as it freezes. It has a maximum of density at 3.98 °C (1000 kg/m3), whereas the density of ice is 917 kg/m3. It differs by about 9% and therefore ice floats on liquid waterSee also: How density influences reactor reactivity
We hope, this article, Change of Density, helps you. If so, give us a like in the sidebar. Main purpose of this website is to help the public to learn some interesting and important information about radiation and dosimeters.