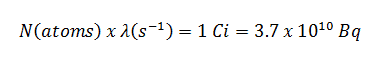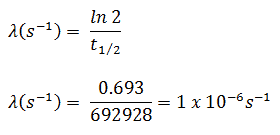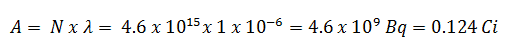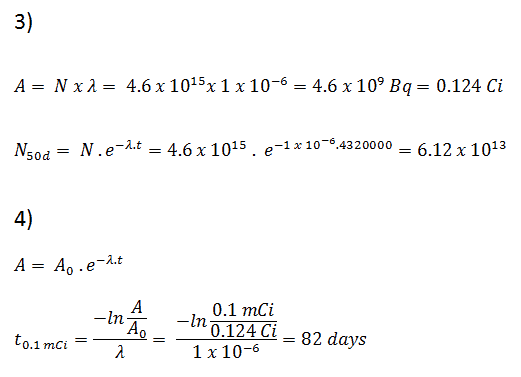The original unit for measuring the amount of radioactivity was the curie (symbol Ci), which is a non-SI unit of radioactivity defined in 1910. A curie was originally named in honour of Pierre Curie, but was considered at least by some to be in honour of Marie Curie as well. A curie was originally defined as equivalent to the number of disintegrations that one gram of radium-226 will undergo in one second. Currently, a curie is defined as 1Ci = 3.7 x 1010 disintegrations per second. Therefore:
1Ci = 3.7 x 1010 Bq = 37 GBq
One curie is a large amount of activity. The typical human body contains roughly 0.1 μCi (14 mg) of naturally occurring potassium-40. As well, a human body containing 16 kg of carbon would also have about 0.1 μCi of carbon-14 (24 nanograms). Activities measured in a nuclear power plant (except irradiated fuel) often have usually lower activity than curie, and the following multiples are often used:
1 mCi (milicurie) = 1E-3 Ci
1 µCi (microcurie) = 1E-6 Ci
While its continued use is discouraged by many institutions, the curie is still widely used throughout the government, industry and medicine in the world.
Curie – Examples
The relationship between half-life and the amount of a radionuclide required to give an activity of one curie is shown in the figure. This amount of material can be calculated using λ, which is the decay constant of certain nuclide:
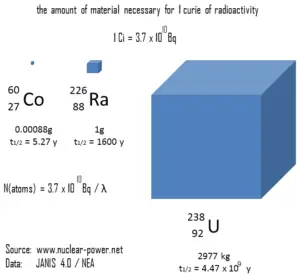 The following figure illustrates the amount of material necessary for 1 curie of radioactivity. It is obvious, that the longer the half-life, the greater the quantity of radionuclide needed to produce the same activity. Of course, the longer lived substance will remain radioactive for a much longer time. As can be seen, the amount of material necessary for 1 curie of radioactivity can vary from an amount too small to be seen (0.00088 gram of cobalt-60), through 1 gram of radium-226, to almost three tons of uranium-238.
The following figure illustrates the amount of material necessary for 1 curie of radioactivity. It is obvious, that the longer the half-life, the greater the quantity of radionuclide needed to produce the same activity. Of course, the longer lived substance will remain radioactive for a much longer time. As can be seen, the amount of material necessary for 1 curie of radioactivity can vary from an amount too small to be seen (0.00088 gram of cobalt-60), through 1 gram of radium-226, to almost three tons of uranium-238.
Example – Calculation of Radioactivity
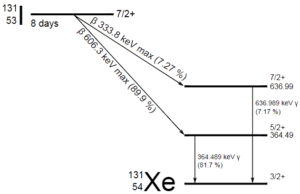 A sample of material contains 1 mikrogram of iodine-131. Note that, iodine-131 plays a major role as a radioactive isotope present in nuclear fission products, and it a major contributor to the health hazards when released into the atmosphere during an accident. Iodine-131 has a half-life of 8.02 days.
A sample of material contains 1 mikrogram of iodine-131. Note that, iodine-131 plays a major role as a radioactive isotope present in nuclear fission products, and it a major contributor to the health hazards when released into the atmosphere during an accident. Iodine-131 has a half-life of 8.02 days.
Calculate:
- The number of iodine-131 atoms initially present.
- The activity of the iodine-131 in curies.
- The number of iodine-131 atoms that will remain in 50 days.
- The time it will take for the activity to reach 0.1 mCi.
Solution:
- The number of atoms of iodine-131 can be determined using isotopic mass as below.
NI-131 = mI-131 . NA / MI-131
NI-131 = (1 μg) x (6.02×1023 nuclei/mol) / (130.91 g/mol)
NI-131 = 4.6 x 1015 nuclei
- The activity of the iodine-131 in curies can be determined using its decay constant:
The iodine-131 has half-live of 8.02 days (692928 sec) and therefore its decay constant is:
Using this value for the decay constant we can determine the activity of the sample:
3) and 4) The number of iodine-131 atoms that will remain in 50 days (N50d) and the time it will take for the activity to reach 0.1 mCi can be calculated using the decay law:
As can be seen, after 50 days the number of iodine-131 atoms and thus the activity will be about 75 times lower. After 82 days the activity will be approximately 1200 times lower. Therefore, the time of ten half-lives (factor 210 = 1024) is widely used to define residual activity.
We hope, this article, Curie – Unit of Radioactivity, helps you. If so, give us a like in the sidebar. Main purpose of this website is to help the public to learn some interesting and important information about radiation and dosimeters.