Isotones
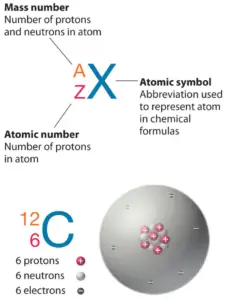 In nuclear physics and nuclear chemistry, the various species of atoms whose nuclei contain particular numbers of protons and neutrons are called nuclides. Nuclides are also characterized by its nuclear energy states (e.g. metastable nuclide 242mAm). Each nuclide is denoted by chemical symbol of the element (this specifies Z) with the atomic mass number as superscript. Hydrogen (H), for example , consist of one electron and one proton. The number of neutrons in a nucleus is known as the neutron number and is given the symbol N. The total number of nucleons, that is, protons and neutrons in a nucleus, is equal to Z + N = A, where A is called the atomic mass number.
In nuclear physics and nuclear chemistry, the various species of atoms whose nuclei contain particular numbers of protons and neutrons are called nuclides. Nuclides are also characterized by its nuclear energy states (e.g. metastable nuclide 242mAm). Each nuclide is denoted by chemical symbol of the element (this specifies Z) with the atomic mass number as superscript. Hydrogen (H), for example , consist of one electron and one proton. The number of neutrons in a nucleus is known as the neutron number and is given the symbol N. The total number of nucleons, that is, protons and neutrons in a nucleus, is equal to Z + N = A, where A is called the atomic mass number.
Isotones are nuclides that have the same neutron number and are therefore different elements, since they must differ in the number of protons. Therefore, isotones must be different chemical elements. For example, carbon – 13 and boron – 12 are isotones, since both nuclei contain 7 neutrons. The name isotone has been derived from the name isotope by changing the “p” in “isotope” from “p” for “proton” to “n” for “neutron”.
The nuclear properties (atomic mass, nuclear cross-sections) of the element are determined by the number of protons and number of neutrons (neutron number). For example, actinides with odd neutron number are usually fissile (fissionable with slow neutrons) while actinides with even neutron number are usually not fissile (but are fissionable with fast neutrons). Heavy nuclei with an even number of protons and an even number of neutrons are (due to Pauli exclusion principle) very stable thanks to the occurrence of ‘paired spin’. On the other hand, nuclei with an odd number of protons and neutrons are mostly unstable (i.e. radioactive). Neutron numbers for which there are no stable isotones are 19, 21, 35, 39, 45, 61, 89, 115, 123, and 127 or more.
See also: Magic Numbers
We hope, this article, Isotone – Nuclide, helps you. If so, give us a like in the sidebar. Main purpose of this website is to help the public to learn some interesting and important information about radiation and dosimeters.