Energy Conservation in Nuclear Fission
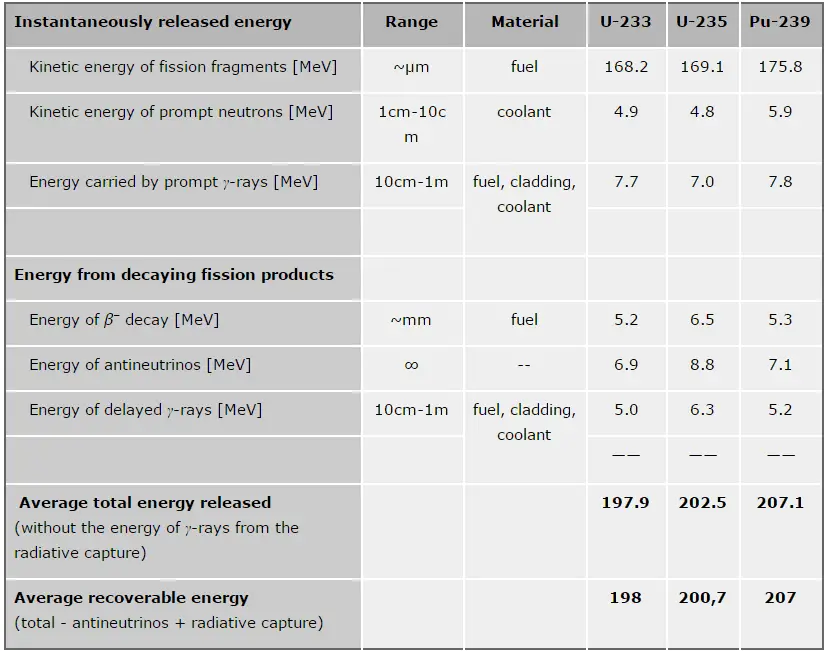 In general, the nuclear fission results in the release of enormous quantities of energy. The amount of energy depends strongly on the nucleus to be fissioned and also depends strongly on the kinetic energy of an incident neutron. In order to calculate the power of a reactor, it is necessary to be able precisely identify the individual components of this energy. At first, it is important to distinguish between the total energy released and the energy that can be recovered in a reactor.
In general, the nuclear fission results in the release of enormous quantities of energy. The amount of energy depends strongly on the nucleus to be fissioned and also depends strongly on the kinetic energy of an incident neutron. In order to calculate the power of a reactor, it is necessary to be able precisely identify the individual components of this energy. At first, it is important to distinguish between the total energy released and the energy that can be recovered in a reactor.
The total energy released in fission can be calculated from binding energies of initial target nucleus to be fissioned and binding energies of fission products. But not all the total energy can be recovered in a reactor. For example, about 10 MeV is released in the form of neutrinos (in fact antineutrinos). Since the neutrinos are weakly interacting (with extremely low cross-section of any interaction), they do not contribute to the energy that can be recovered in a reactor.
See also: Energy Release from Fission
We hope, this article, Energy Conservation in Nuclear Fission, helps you. If so, give us a like in the sidebar. Main purpose of this website is to help the public to learn some interesting and important information about radiation and dosimeters.