Spectrum of beta particles
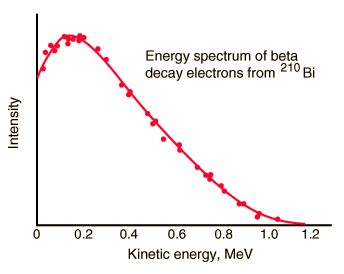
In the process of beta decay, either an electron or a positron is emitted. This emission is accompanied by the emission of antineutrino (β- decay) or neutrino (β+ decay), which shares energy and momentum of the decay. The beta emission has a characteristic spectrum. This characteristic spectrum is caused by the fact that either a neutrino or an antineutrino is emitted with emission of beta particle. The shape of this energy curve depends on what fraction of the reaction energy (Q value-the amount of energy released by the reaction) is carried by the massive particle. Beta particles can therefore be emitted with any kinetic energy ranging from 0 to Q. By 1934, Enrico Fermi had developed a Fermi theory of beta decay, which predicted the shape of this energy curve.
We hope, this article, Spectrum of Beta Particles, helps you. If so, give us a like in the sidebar. Main purpose of this website is to help the public to learn some interesting and important information about radiation and dosimeters.