Hydrogen
Nonmetals
Helium
Noble gas
Lithium
Alkali metal
Beryllium
Alkaline earth metal
Boron
Metalloids
Carbon
Nonmetals
Nitrogen
Nonmetals
Oxygen
Nonmetals
Fluorine
Nonmetals
Neon
Noble gas
Sodium
Alkali metal
Magnesium
Alkaline earth metal
Aluminium
Post-transition metals
Silicon
Metalloids
Phosphorus
Nonmetal
Sulfur
Nonmetal
Chlorine
Nonmetal
Argon
Noble gas
Potassium
Alkali metal
Calcium
Alkaline earth metal
Scandium
Transition metals
Titanium
Transition metals
Vanadium
Transition metals
Chromium
Transition metals
Manganese
Transition metals
Iron
Transition metals
Cobalt
Transition metals
Nickel
Transition metals
Copper
Transition metals
Zinc
Transition metals
Gallium
Post-transition metals
Germanium
Metalloids
Arsenic
Metalloids
Selenium
Nonmetal
Bromine
Nonmetal
Krypton
Noble gas
Rubidium
Alkali metals
Strontium
Alkaline earth metals
Yttrium
Transition metals
Zirconium
Transition metals
Niobium
Transition metals
Molybdenum
Transition metals
Technetium
Transition metals
Ruthenium
Transition metals
Rhodium
Transition metals
Palladium
Transition metals
Silver
Transition metals
Cadmium
Transition metals
Indium
Post-transition metals
Tin
Post-transition metals
Antimony
Metalloids
Tellurium
Metalloids
Iodine
Nonmetal
Xenon
Noble gas
Caesium
Alkali metals
Lanthanoids
Hafnium
Transition metals
Tantalum
Transition metals
Tungsten
Transition metals
Rhenium
Transition metals
Osmium
Transition metals
Iridium
Transition metals
Platinum
Transition metals
Gold
Transition metals
Mercury
Transition metals
Thallium
Post-transition metals
Lead
Post-transition metals
Bismuth
Post-transition metals
Polonium
Post-transition metals
Astatine
Metalloids
Radon
Noble gas
Francium
Alkali metal
Radium
Alkaline earth metal
Actinoids
Rutherfordium
Transition metal
Dubnium
Transition metal
Seaborgium
Transition metal
Bohrium
Transition metal
Hassium
Transition metal
Meitnerium
Darmstadtium
Roentgenium
Copernicium
Nihonium
Flerovium
Moscovium
Livermorium
Tennessine
Oganesson
Lanthanum
Lanthanoids
Cerium
Lanthanoids
Praseodymium
Lanthanoids
Neodymium
Lanthanoids
Promethium
Lanthanoids
Samarium
Lanthanoids
Europium
Lanthanoids
Gadolinium
Lanthanoids
Terbium
Lanthanoids
Dysprosium
Lanthanoids
Holmium
Lanthanoids
Erbium
Lanthanoids
Thulium
Lanthanoids
Ytterbium
Lanthanoids
Lutetium
Lanthanoids
Actinium
Actinoids
Thorium
Actinoids
Protactinium
Actinoids
Uranium
Actinoids
Neptunium
Actinoids
Plutonium
Actinoids
Americium
Actinoids
Curium
Actinoids
Berkelium
Actinoids
Californium
Actinoids
Einsteinium
Actinoids
Fermium
Actinoids
Mendelevium
Actinoids
Nobelium
Actinoids
Lawrencium
Actinoids
What is Argon
Argon is a chemical element with atomic number 18 which means there are 18 protons and 18 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical symbol for Argon is Ar.
Argon is the third-most abundant gas in the Earth’s atmosphere, at 0.934% (9340 ppmv). It is more than twice as abundant as water vapor (which averages about 4000 ppmv, but varies greatly), 23 times as abundant as carbon dioxide (400 ppmv), and more than 500 times as abundant as neon (18 ppmv). Argon is mostly used as an inert shielding gas in welding and other high-temperature industrial processes where ordinarily unreactive substances become reactive; for example, an argon atmosphere is used in graphite electric furnaces to prevent the graphite from burning.
Argon – Properties
| Element | Argon |
|---|---|
| Atomic Number | 18 |
| Symbol | Ar |
| Element Category | Noble Gas |
| Phase at STP | Gas |
| Atomic Mass [amu] | 39.948 |
| Density at STP [g/cm3] | 1.784 |
| Electron Configuration | [Ne] 3s2 3p6 |
| Possible Oxidation States | 0 |
| Electron Affinity [kJ/mol] | — |
| Electronegativity [Pauling scale] | — |
| 1st Ionization Energy [eV] | 15.7596 |
| Year of Discovery | 1894 |
| Discoverer | Ramsay, Sir William & Strutt, John (Lord Rayleigh) |
| Thermal properties | |
| Melting Point [Celsius scale] | -189.2 |
| Boiling Point [Celsius scale] | -185.7 |
| Thermal Expansion µm/(m·K) | — |
| Thermal Conductivity [W/m K] | 0.01772 |
| Specific Heat [J/g K] | 0.52 |
| Heat of Fusion [kJ/mol] | 1.188 |
| Heat of Vaporization [kJ/mol] | 6.447 |
Atomic Number of Argon
Argon is a chemical element with atomic number 18 which means there are 18 protons and 18 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical symbol for Argon is Ar.
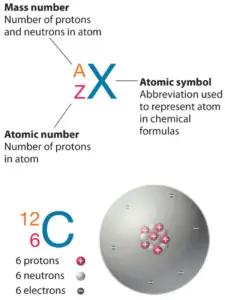 The atom consist of a small but massive nucleus surrounded by a cloud of rapidly moving electrons. The nucleus is composed of protons and neutrons. Total number of protons in the nucleus is called the atomic number of the atom and is given the symbol Z. The total electrical charge of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (elementary charge) equals to 1,602 x 10-19 coulombs. In a neutral atom there are as many electrons as protons moving about nucleus. It is the electrons that are responsible for the chemical bavavior of atoms, and which identify the various chemical elements.
The atom consist of a small but massive nucleus surrounded by a cloud of rapidly moving electrons. The nucleus is composed of protons and neutrons. Total number of protons in the nucleus is called the atomic number of the atom and is given the symbol Z. The total electrical charge of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (elementary charge) equals to 1,602 x 10-19 coulombs. In a neutral atom there are as many electrons as protons moving about nucleus. It is the electrons that are responsible for the chemical bavavior of atoms, and which identify the various chemical elements.
See also: Atomic Number – Does it conserve in a nuclear reaction?
Atomic Number and Chemical Properties
Every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. The chemical properties of the atom are determined by the number of protons, in fact, by number and arrangement of electrons. The configuration of these electrons follows from the principles of quantum mechanics. The number of electrons in each element’s electron shells, particularly the outermost valence shell, is the primary factor in determining its chemical bonding behavior. In the periodic table, the elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number Z.
It is the Pauli exclusion principle that requires the electrons in an atom to occupy different energy levels instead of them all condensing in the ground state. The ordering of the electrons in the ground state of multielectron atoms, starts with the lowest energy state (ground state) and moves progressively from there up the energy scale until each of the atom’s electrons has been assigned a unique set of quantum numbers. This fact has key implications for the building up of the periodic table of elements.
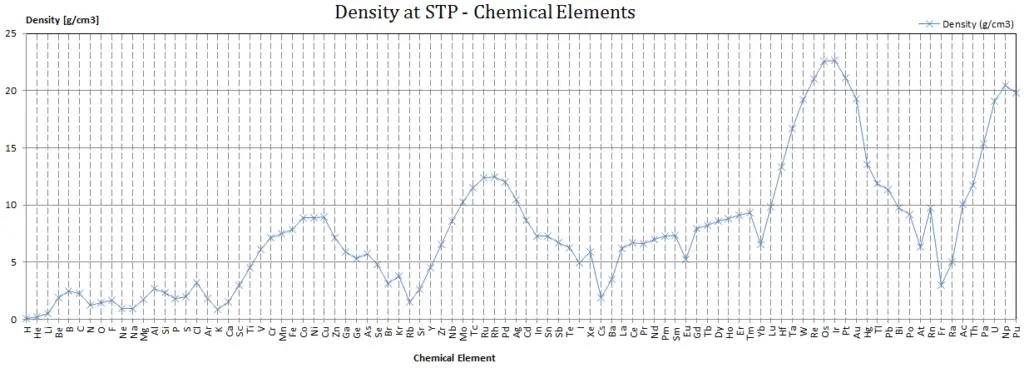
 Density of Argon
Density of Argon
Density of Argon is 1.784g/cm3.
Typical densities of various substances are at atmospheric pressure.
Density is defined as the mass per unit volume. It is an intensive property, which is mathematically defined as mass divided by volume:
ρ = m/V
In words, the density (ρ) of a substance is the total mass (m) of that substance divided by the total volume (V) occupied by that substance. The standard SI unit is kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m3). The Standard English unit is pounds mass per cubic foot (lbm/ft3).
Density – Atomic Mass and Atomic Number Density
Since the density (ρ) of a substance is the total mass (m) of that substance divided by the total volume (V) occupied by that substance, it is obvious, the density of a substance strongly depends on its atomic mass and also on the atomic number density (N; atoms/cm3),
- Atomic Weight. The atomic mass is carried by the atomic nucleus, which occupies only about 10-12 of the total volume of the atom or less, but it contains all the positive charge and at least 99.95% of the total mass of the atom. Therefore it is determined by the mass number (number of protons and neutrons).
- Atomic Number Density. The atomic number density (N; atoms/cm3), which is associated with atomic radii, is the number of atoms of a given type per unit volume (V; cm3) of the material. The atomic number density (N; atoms/cm3) of a pure material having atomic or molecular weight (M; grams/mol) and the material density (⍴; gram/cm3) is easily computed from the following equation using Avogadro’s number (NA = 6.022×1023 atoms or molecules per mole):
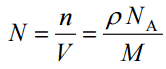
Since nucleons (protons and neutrons) make up most of the mass of ordinary atoms, the density of normal matter tends to be limited by how closely we can pack these nucleons and depends on the internal atomic structure of a substance. The densest material found on earth is the metal osmium, but its density pales by comparison to the densities of exotic astronomical objects such as white dwarf stars and neutron stars.
If we include man made elements, the densest so far is Hassium. Hassium is a chemical element with symbol Hs and atomic number 108. It is a synthetic element (first synthesised at Hasse in Germany) and radioactive. The most stable known isotope, 269Hs, has a half-life of approximately 9.7 seconds. It has an estimated density of 40.7 x 103 kg/m3. The density of Hassium results from its high atomic weight and from the significant decrease in ionic radii of the elements in the lanthanide series, known as lanthanide and actinide contraction.
Density – Pressure and Temperature
The density of a material varies with temperature and pressure. This variation is typically small for solids and liquids but much greater for gases. Most materials expand when their temperatures increase. Rising temperatures make the liquid expand in a liquid-in-tube thermometer and bend bimetallic strips. As a result of this expansion, the density of most materials decreases. This effect is caused by a decrease in the atomic number density. This dependence is usually expressed by the coefficient of linear or volume expansion.
Increasing the pressure on an material (especially for liquids or gases) decreases the volume of the object and thus increases its density via the atomic number density. Compressibility (also known as the coefficient of compressibility is a measure of the relative volume change of a fluid or solid as a response to a pressure (or mean stress) change.
See also: What is Density
See also: Densest Materials of the Earth
Electron Configuration and Oxidation States of Argon
Electron configuration of Argon is [Ne] 3s2 3p6.
Possible oxidation states are 0.
Electron Configuration
The periodic table is a tabular display of the chemical elements organized on the basis of their atomic numbers, electron configurations, and chemical properties. The electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements.
Every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. The chemical properties of the atom are determined by the number of protons, in fact, by number and arrangement of electrons. The configuration of these electrons follows from the principles of quantum mechanics. The number of electrons in each element’s electron shells, particularly the outermost valence shell, is the primary factor in determining its chemical bonding behavior. In the periodic table, the elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number Z.
It is the Pauli exclusion principle that requires the electrons in an atom to occupy different energy levels instead of them all condensing in the ground state. The ordering of the electrons in the ground state of multielectron atoms, starts with the lowest energy state (ground state) and moves progressively from there up the energy scale until each of the atom’s electrons has been assigned a unique set of quantum numbers. This fact has key implications for the building up of the periodic table of elements.
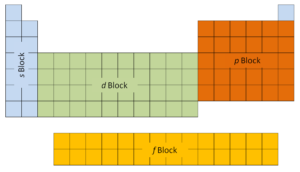 The first two columns on the left side of the periodic table are where the s subshells are being occupied. Because of this, the first two rows of the periodic table are labeled the s block. Similarly, the p block are the right-most six columns of the periodic table, the d block is the middle 10 columns of the periodic table, while the f block is the 14-column section that is normally depicted as detached from the main body of the periodic table. It could be part of the main body, but then the periodic table would be rather long and cumbersome.
The first two columns on the left side of the periodic table are where the s subshells are being occupied. Because of this, the first two rows of the periodic table are labeled the s block. Similarly, the p block are the right-most six columns of the periodic table, the d block is the middle 10 columns of the periodic table, while the f block is the 14-column section that is normally depicted as detached from the main body of the periodic table. It could be part of the main body, but then the periodic table would be rather long and cumbersome.
For atoms with many electrons, this notation can become lengthy and so an abbreviated notation is used. The electron configuration can be visualized as the core electrons, equivalent to the noble gas of the preceding period, and the valence electrons (e.g. [Xe] 6s2 for barium).
Oxidation States
Oxidation states are typically represented by integers which may be positive, zero, or negative. Most elements have more than one possible oxidation state. For example, carbon has nine possible integer oxidation states from −4 to +4.
The current IUPAC Gold Book definition of oxidation state is:
“Oxidation state of an atom is the charge of this atom after ionic approximation of its heteronuclear bonds…”
and the term oxidation number is nearly synonymous. An element that is not combined with any other different elements has an oxidation state of 0. Oxidation state 0 occurs for all elements – it is simply the element in its elemental form. An atom of an element in a compound will have a positive oxidation state if it has had electrons removed. Similarly, adding electrons results in a negative oxidation state. We have also distinguish between the possible and common oxidation states of every element. For example, silicon has nine possible integer oxidation states from −4 to +4, but only -4, 0 and +4 are common oxidation states.
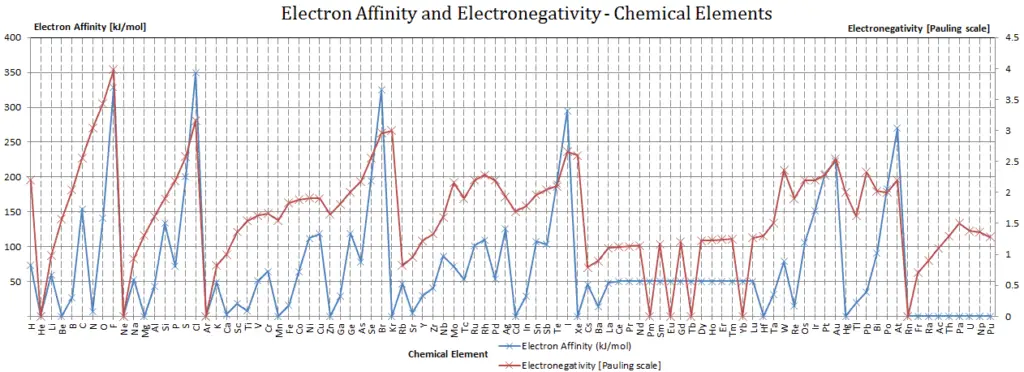
Electron Affinity and Electronegativity of Argon
Electron affinity of Argon is — kJ/mol.
Electronegativity of Argon is —.
Electron Affinity
In chemistry and atomic physics, the electron affinity of an atom or molecule is defined as:
the change in energy (in kJ/mole) of a neutral atom or molecule (in the gaseous phase) when an electron is added to the atom to form a negative ion.
X + e– → X– + energy Affinity = – ∆H
In other words, it can be expressed as the neutral atom’s likelihood of gaining an electron. Note that, ionization energies measure the tendency of a neutral atom to resist the loss of electrons. Electron affinities are more difficult to measure than ionization energies.
An atom of Argon in the gas phase, for example, gives off energy when it gains an electron to form an ion of Argon.
Ar + e– → Ar– – ∆H = Affinity = — kJ/mol
To use electron affinities properly, it is essential to keep track of sign. When an electron is added to a neutral atom, energy is released. This affinity is known as the first electron affinity and these energies are negative. By convention, the negative sign shows a release of energy. However, more energy is required to add an electron to a negative ion which overwhelms any the release of energy from the electron attachment process. This affinity is known as the second electron affinity and these energies are positive.
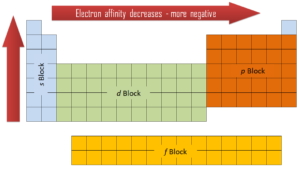 Electron affinity can be either positive or negative value. The greater the negative value, the more stable the anion is. Although affinity varies greatly across the periodic table, some patterns emerge. Generally, the elements on the right side of the periodic table will have large negative electron affinity. The electron affinities will become less negative as you go from the top to the bottom of the periodic table. However, nitrogen, oxygen, and fluorine do not follow this trend. Moreover, nonmetals have more positive affinity than metals. Atoms whose anions are more stable than neutral atoms have a greater affinity. Chlorine most strongly attracts extra electrons, while neon most weakly attracts an extra electron.
Electron affinity can be either positive or negative value. The greater the negative value, the more stable the anion is. Although affinity varies greatly across the periodic table, some patterns emerge. Generally, the elements on the right side of the periodic table will have large negative electron affinity. The electron affinities will become less negative as you go from the top to the bottom of the periodic table. However, nitrogen, oxygen, and fluorine do not follow this trend. Moreover, nonmetals have more positive affinity than metals. Atoms whose anions are more stable than neutral atoms have a greater affinity. Chlorine most strongly attracts extra electrons, while neon most weakly attracts an extra electron.
Affinities of Non metals vs. Affinities of Metals
- Metals: Metals like to lose valence electrons to form cations to have a fully stable shell. The electron affinity of metals is lower than that of nonmetals. Mercury most weakly attracts an extra electron.
- Nonmetals: Generally, nonmetals have more positive electron affinity than metals. Nonmetals like to gain electrons to form anions to have a fully stable electron shell. Chlorine most strongly attracts extra electrons. The electron affinities of the noble gases have not been conclusively measured, so they may or may not have slightly negative values.
Electronegativity
Electronegativity, symbol χ, is a chemical property that describes the tendency of an atom to attract electrons towards this atom. For this purposes, a dimensionless quantity the Pauling scale, symbol χ, is the most commonly used.
The electronegativity of Argon is: χ = —
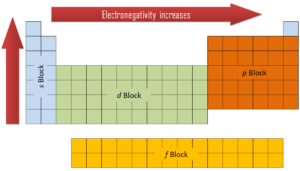 In general, an atom’s electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the distance at which its valence electrons reside from the charged nucleus. The higher the associated electronegativity number, the more an element or compound attracts electrons towards it. The most electronegative atom, fluorine, is assigned a value of 4.0, and values range down to cesium and francium which are the least electronegative at 0.7. Electronegativity is related with ionization energy and electron affinity. Electrons with low ionization energies have low electronegativities because their nuclei do not exert a strong attractive force on electrons. Elements with high ionization energies have high electronegativities due to the strong pull exerted by the positive nucleus on the negative electrons. Therefore the electronegativity is greatest at the top-right of the periodic table and decreases toward the bottom-left.
In general, an atom’s electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the distance at which its valence electrons reside from the charged nucleus. The higher the associated electronegativity number, the more an element or compound attracts electrons towards it. The most electronegative atom, fluorine, is assigned a value of 4.0, and values range down to cesium and francium which are the least electronegative at 0.7. Electronegativity is related with ionization energy and electron affinity. Electrons with low ionization energies have low electronegativities because their nuclei do not exert a strong attractive force on electrons. Elements with high ionization energies have high electronegativities due to the strong pull exerted by the positive nucleus on the negative electrons. Therefore the electronegativity is greatest at the top-right of the periodic table and decreases toward the bottom-left.
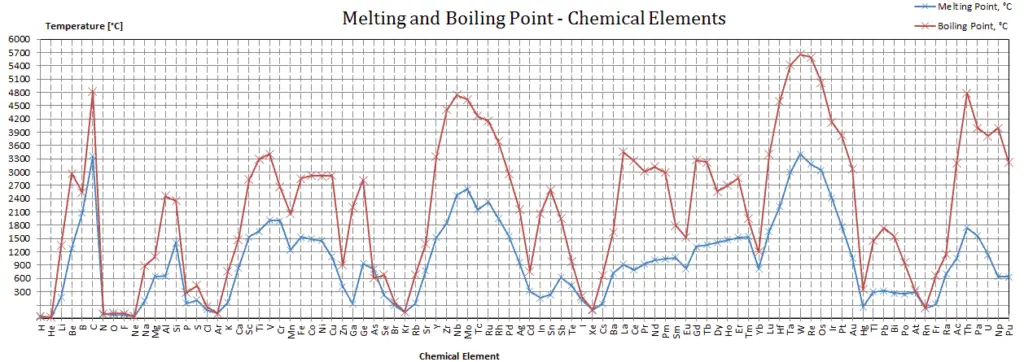
Argon – Melting Point and Boiling Point
Melting point of Argon is -189.2°C.
Boiling point of Argon is -185.7°C.
Note that, these points are associated with the standard atmospheric pressure.
Boiling Point
In general, boiling is a phase change of a substance from the liquid to the gas phase. The boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which this phase change (boiling or vaporization) occurs. The temperature at which vaporization (boiling) starts to occur for a given pressure is also known as the saturation temperature and at this conditions a mixture of vapor and liquid can exist together. The liquid can be said to be saturated with thermal energy. Any addition of thermal energy results in a phase transition. At the boiling point the two phases of a substance, liquid and vapor, have identical free energies and therefore are equally likely to exist. Below the boiling point, the liquid is the more stable state of the two, whereas above the gaseous form is preferred. The pressure at which vaporization (boiling) starts to occur for a given temperature is called the saturation pressure. When considered as the temperature of the reverse change from vapor to liquid, it is referred to as the condensation point.
As can be seen, the boiling point of a liquid varies depending upon the surrounding environmental pressure. A liquid in a partial vacuum has a lower boiling point than when that liquid is at atmospheric pressure. A liquid at high pressure has a higher boiling point than when that liquid is at atmospheric pressure. For example, water boils at 100°C (212°F) at sea level, but at 93.4°C (200.1°F) at 1900 metres (6,233 ft) altitude. On the other hand, water boils at 350°C (662°F) at 16.5 MPa (typical pressure of PWRs).
In the periodic table of elements, the element with the lowest boiling point is helium. Both the boiling points of rhenium and tungsten exceed 5000 K at standard pressure. Since it is difficult to measure extreme temperatures precisely without bias, both have been cited in the literature as having the higher boiling point.
Melting Point
In general, melting is a phase change of a substance from the solid to the liquid phase. The melting point of a substance is the temperature at which this phase change occurs. The melting point also defines a condition in which the solid and liquid can exist in equilibrium. Adding a heat will convert the solid into a liquid with no temperature change. At the melting point the two phases of a substance, liquid and vapor, have identical free energies and therefore are equally likely to exist. Below the melting point, the solid is the more stable state of the two, whereas above the liquid form is preferred. The melting point of a substance depends on pressure and is usually specified at standard pressure. When considered as the temperature of the reverse change from liquid to solid, it is referred to as the freezing point or crystallization point.
See also: Melting Point Depression
The first theory explaining mechanism of melting in the bulk was proposed by Lindemann, who used vibration of atoms in the crystal to explain the melting transition. Solids are similar to liquids in that both are condensed states, with particles that are far closer together than those of a gas. The atoms in a solid are tightly bound to each other, either in a regular geometric lattice (crystalline solids, which include metals and ordinary ice) or irregularly (an amorphous solid such as common window glass), and are typically low in energy. The motion of individual atoms, ions, or molecules in a solid is restricted to vibrational motion about a fixed point. As a solid is heated, its particles vibrate more rapidly as the solid absorbs kinetic energy. At some point the amplitude of vibration becomes so large that the atoms start to invade the space of their nearest neighbors and disturb them and the melting process initiates. The melting point is the temperature at which the disruptive vibrations of the particles of the solid overcome the attractive forces operating within the solid.
As with boiling points, the melting point of a solid is dependent on the strength of those attractive forces. For example, sodium chloride (NaCl) is an ionic compound that consists of a multitude of strong ionic bonds. Sodium chloride melts at 801°C. On the other hand, ice (solid H2O) is a molecular compound whose molecules are held together by hydrogen bonds, which is effectively a strong example of an interaction between two permanent dipoles. Though hydrogen bonds are the strongest of the intermolecular forces, the strength of hydrogen bonds is much less than that of ionic bonds. The melting point of ice is 0 °C.
Covalent bonds often result in the formation of small collections of better-connected atoms called molecules, which in solids and liquids are bound to other molecules by forces that are often much weaker than the covalent bonds that hold the molecules internally together. Such weak intermolecular bonds give organic molecular substances, such as waxes and oils, their soft bulk character, and their low melting points (in liquids, molecules must cease most structured or oriented contact with each other).
Argon – Crystal Structure
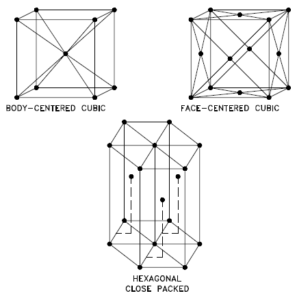
A possible crystal structure of Argon is face-centered cubic structure.
In metals, and in many other solids, the atoms are arranged in regular arrays called crystals. A crystal lattice is a repeating pattern of mathematical points that extends throughout space. The forces of chemical bonding causes this repetition. It is this repeated pattern which control properties like strength, ductility, density, conductivity (property of conducting or transmitting heat, electricity, etc.), and shape. There are 14 general types of such patterns known as Bravais lattices.
The three most common basic crystal patterns are:
- Body-centered Cubic. In a body-centered cubic (BCC) arrangement of atoms, the unit cell consists of eight atoms at the corners of a cube and one atom at the body center of the cube. In a body-centered cubic arrangement, a unit cell contains (8 corner atoms × ⅛) + (1 center atom × 1) = 2 atoms. The packing is more efficient (68%) than simple cubic and the structure is a common one for alkali metals and early transition metals. Metals containing BCC structures include ferrite, chromium, vanadium, molybdenum, and tungsten. These metals possess high strength and low ductility.
- Face-centered Cubic.In a face-centered cubic (FCC) arrangement of atoms, the unit cell consists of eight atoms at the corners of a cube and one atom at the center of each of the faces of the cube. In a face-centered cubic arrangement, a unit cell contains (8 corner atoms × ⅛) + (6 face atoms × ½) = 4 atoms. This structure, along with its hexagonal relative (hcp), has the most efficient packing (74%). Metals containing FCC structures include austenite, aluminum, copper, lead, silver, gold, nickel, platinum, and thorium. These metals possess low strength and high ductility.
- Hexagonal Close-packed. In a hexagonal close-packed (HCP) arrangement of atoms, the unit cell consists of three layers of atoms. The top and bottom layers contain six atoms at the corners of a hexagon and one atom at the center of each hexagon. The middle layer contains three atoms nestled between the atoms of the top and bottom layers, hence, the name close-packed. Hexagonal close packed (hcp) is one of the two simple types of atomic packing with the highest density, the other being the face centered cubic (fcc). However, unlike the fcc, it is not a Bravais lattice as there are two nonequivalent sets of lattice points. Metals containing HCP structures include beryllium, magnesium, zinc, cadmium, cobalt, thallium, and zirconium. HCP metals are not as ductile as FCC metals.
–